अरबी भाषा
अरबी (اَلْعَرَبِيَّةُ; अल अरबिय्याह) सामी भासा परिवार के एगो भासा हऽ।[4] ई अरब के संपर्क भासा हऽ।[5] एकर नांव अरब लोग के नांव प पड़ल बा। प्राचीन यूनान के लोग, अरब शब्द के प्रयोग ऊ जगह प रहे वला लोग बदे करत रहे, जवन पक्खिम मे पुरबी मिस्र, पूरब मे मेसोपोटेमिया, उत्तर मे लेबनान पर्वतमाला आ आ सीरिया से घेराइल रहे।[6] अंतर्राष्ट्रीय मानकीकरण संस्था अरबी भाषा के, मानक रूप "आधुनिक मानक अरबी" संगे ओकर तीस गो रूपन के अलग अलग कोड दिहले बा।[7] आधुनिक मानक अरबी के साहित्यिक अरबी कहल जाला काहे की ऊ पुरान अरबी के आधुनिक रूप हऽ।
| अरबी | |
|---|---|
| اَلْعَرَبِيَّةُ अल अरबिय्याह | |
 अल अरबिय्याह in written Arabic (Naskh script) | |
| उच्चारण | /ˈʕarabiː/, /alʕaraˈbijːa/ |
| मूलभाषा बाटे | अरब लीग के देसन मे, पड़ोस के देसन आ एशिया, अफ्रिका आ युरोप के कुछ भागन मे अल्पसंख्यक भासा |
| नृजातीयता | Arabs, Arab-Berbers, Afro-Arabs, among others |
मूल बोले वाला | 310 million, all varieties (2011–2016)[1] 270 million L2 speakers of Standard (Modern) Arabic[1] |
प्रारंभिक रूप | |
स्टैंडर्ड रूप | |
| बोली सभ | |
| •Arabic Alphabet •Arabic Braille •Arabizi | |
| Signed Arabic (different national forms) | |
| ऑफिशियल स्टेटस | |
सरकारी भाषा बाटे | International Organizations
|
अल्पसंख्यक पहिचान वाली भाषा बाटे | |
| नियमित कइल जाले | लिस्ट
|
| भाषा कोड | |
| ISO 639-1 | ar |
| ISO 639-2 | ara |
| ISO 639-3 | ara – inclusive codeIndividual codes: arq – Algerian Arabicaao – Algerian Saharan Arabicxaa – Andalusian Arabicbbz – Babalia Creole Arabicabv – Baharna Arabicshu – Chadian Arabicacy – Cypriot Arabicadf – Dhofari Arabicavl – Eastern Egyptian Bedawi Arabicarz – Egyptian Arabicafb – Gulf Arabicayh – Hadrami Arabicacw – Hijazi Arabicayl – Libyan Arabicacm – Mesopotamian Arabicary – Moroccan Arabicars – Najdi Arabicapc – North Levantine Arabicayp – North Mesopotamian Arabicacx – Omani Arabicaec – Saidi Arabicayn – Sanaani Arabicssh – Shihhi Arabicsqr – Siculo Arabicajp – South Levantine Arabicarb – Standard Arabicapd – Sudanese Arabicpga – Sudanese Creole Arabicacq – Taizzi-Adeni Arabicabh – Tajiki Arabic |
| Glottolog | arab1395[3] |
| Linguasphere | 12-AAC |
 Dispersion of native Arabic speakers | |
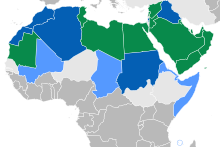 Use of Arabic as the national language (green), as an official language (dark blue) and as a regional/minority language (light blue) | |
सन्दर्भ
संपादन करीं- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Arabic – Ethnologue". Ethnologue. Simons, Gary F. and Charles D. Fennig (eds.). 2018. Ethnologue: Languages of the World, 21st edition. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- ↑ "Basic Law: Israel - The Nation State of the Jewish People" (PDF). Knesset. 2018-07-19. Retrieved 2021-01-13.
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Arabic". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011.
- ↑ "Al-Jallad. The earliest stages of Arabic and its linguistic classification (Routledge Handbook of Arabic Linguistics, forthcoming)". Archived from the original on 23 October 2017. Retrieved 2016-10-27.
- ↑ Macdonald, Michael C. A. "Arabians, Arabias, and the Greeks_Contact and Perceptions" (अंग्रेजी में): 16–17.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ "Documentation for ISO 639 identifier: ara". Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 20 March 2018.