एड्रेनेलिन
एड्रेनेलिन (Adrenaline) जेकरा के एपिनेफ्राइन (Epinephrine) के नाँव से भी जानल जाला, एगो हार्मोन आ दवाई हवे।[5][6] ई शरीर के विसरल फंक्शन, मने कि अपने आप संचालित होखे वाला अंदरूनी क्रिया सभ, जइसे कि साँस लिहल वगैरह के रेगुलेट करे ला। शरीर में आमतौर प एकर उत्पादन एड्रेनेलिन ग्लैंड में होला आ कुछ मात्रा में ई मेडुला ऑब्लांगाटा के न्यूरान सभ द्वारा उत्पादित कइल जाला। ई हार्मोन के रूप में, लड़े-चाहे-भागे के रिस्पांस में बहुत महत्व के भूमिका वाला चीज हवे, मांसपेशी सभ में खून के बहाव बढ़ा के, दिल के धड़के के गति तेज क के, आँख के पुतरी में फइलाव ले आ के आ खून में शुगर के लेवल रेगुलेट क के ई आपन काम करे ला। ई हार्मोन कई जानवर सभ में पावल जाला आ कुक एक कोशिका वाला जीव सभ में भी मिले ला। पोलैंड के फिजियोलॉजिस्ट नेपोलियन सायबुल्सकी पहिली बेर एकरा के 1895 में आइसोलेट करे में सफल भइल रहलें।
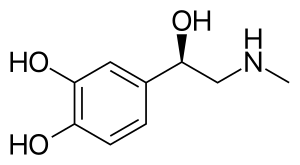 Skeletal formula of adrenaline | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | EpiPen, Adrenaclick, others |
| Other names | Epinephrine, adrenaline, adrenalin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a603002 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Addiction liability | None |
| Routes of administration | IV, IM, endotracheal, IC, nasal, eye drop |
| ATC code | |
| Physiological data | |
| Receptors | Adrenergic receptors |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 15–20%[2][3] |
| Metabolites | Metanephrine[4] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.090 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H13NO3 |
| Molar mass | 183.21 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.283±0.06 g/cm3 @ 20 °C, 760 Torr |
| |
| |
संदर्भ
संपादन करीं- ↑ Andersen AM (1975). "Structural Studies of Metabolic Products of Dopamine. III. Crystal and Molecular Structure of (−)-Adrenaline". Acta Chem. Scand. 29b: 239–244. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.29b-0239.
- ↑ El-Bahr SM, Kahlbacher H, Patzl M, Palme RG (May 2006). "Binding and clearance of radioactive adrenaline and noradrenaline in sheep blood". Veterinary Research Communications. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. 30 (4): 423–32. doi:10.1007/s11259-006-3244-1. PMID 16502110. S2CID 9054777.
- ↑ Franksson G, Anggård E (2009-03-13). "The plasma protein binding of amphetamine, catecholamines and related compounds". Acta Pharmacologica Et Toxicologica. Wiley. 28 (3): 209–14. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0773.1970.tb00546.x. PMID 5468075.
- ↑ Peaston RT, Weinkove C (January 2004). "Measurement of catecholamines and their metabolites". Annals of Clinical Biochemistry. SAGE Publications. 41 (Pt 1): 17–38. doi:10.1258/000456304322664663. PMID 14713382.
- ↑ Lieberman M, Marks A, Peet A (2013). Marks' Basic Medical Biochemistry: A Clinical Approach (4th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 175. ISBN 9781608315727.
- ↑ "(-)-adrenaline". 21 August 2015.
| ई मेडिकल-संबंधी लेख एगो आधार बाटे। जानकारी जोड़ के एकरा के बढ़ावे में विकिपीडिया के मदद करीं। |