पनकउआ
पनकउआ (अंग्रेजी: Great cormorant, बैज्ञानिक नाँव:Phalacrocorax carbo) चिरइन के एगो प्रजाति बाटे। ई समुंदरी चिरई सभ के कोर्मोरैंट परिवार के सदस्य हवे।[2] एकरा बंस के नाँव लैटिनाइज रूप हवे आ एकर उत्पत्ति प्राचीन यूनानी भाषा के φαλακρός (फालाक्रोस, "चंडूल") आ κόραξ (कोराक्स, "कागा") से बाटे आ कार्बो मने लैटिन में "चारकोल" होला।[3]
| पनकउआ | |
|---|---|

| |
| A great comorant in Victoria, Australia. | |
| बैज्ञानिक वर्गीकरण | |
| किंगडम: | Animalia |
| फाइलम: | Chordata |
| क्लास: | Aves |
| ऑर्डर (Order): | Suliformes |
| परिवार: | Phalacrocoracidae |
| जाति (Genus): | Phalacrocorax |
| प्रजाति: | P. carbo |
| दूपद नाँव | |
| Phalacrocorax carbo (Linnaeus, 1758) | |
| |
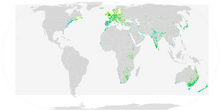
| Global range Year-Round Range Summer Range Winter Range | |
एकरे अंडा देवे के भूगोलीय इलाका पुरानी दुनिया आ उत्तरी अमेरिका के अटलांटिक तट बाटे।
बिबरण
संपादन करींई एक ठो बड़हन आकार के करिया रंग के चिरई हवे आ एकरा आकर में इलाका के हिसाब से बहुत बिबिधता देखे के मिले ला। एकर वजन 1.5 किग्रा (3.3 पाउंड)[4] से 5.3 किग्रा (12 पाउंड) ले बतावल जाला।[5] नर पनकउआ के साइज मादा के तुलना में बड़ा होला आ ई भारी भी होखे लें, एकर सभसे प्रमुख उपप्रजाति (P. c. carbo) यूरोप में पावल जाए वाली (P. c. sinensis) से 10% बड़ा होले।[6] सभसे हल्लुक जर्मनी में पावल जाए वाली (P. c. sinensis) होले, जहाँ 36 गो नर सभ के औसत वजन 2.28 किग्रा (5.0 पाउंड) नापल गइल रहल आ 17 गो मादा सभ के वजन जोखला पर 1.94 किग्रा (4.3 पाउंड) आइल।[7] सभसे भारी वजन प्रिंस एडवर्ड दीप, कनाडा में (P. c. carbo) के रहल जहाँ 11 गो नर सभके औसत वजन 3.68 किग्रा (8.1 पाउंड) आ 11 गो मादा सभके वजन 2.94 किग्रा (6.5 पाउंड) जोखल गइल।[8][9] लंबाई 70 से 102 सेमी (28 से 40 इंच) आ पाँख बिस्तार 121 से 160 सेमी (48 से 63 इंच) बतावल गइल बाटे।[9][10]
इलाका
संपादन करींई बहुत कॉमन चिरई हवे आ समुन्दर आ एश्चुअरी वाला इलाका में पावल जालीं। ढेर उत्तर में पावल जाए वाली चिरई सभ जाड़ा के दिन में समुन्दर के किनारा के सहारे दक्खिन की ओर प्रवास करि जालीं जहाँ पर्याप्त मछरी मिलें।
Behaviour
संपादन करींThe great cormorant breeds mainly on coasts, nesting on cliffs or in trees (which are eventually killed by the droppings), but also increasingly inland. Three or four eggs are laid in a nest of seaweed or twigs.
The great cormorant can dive to considerable depths, but often feeds in shallow water. It frequently brings prey to the surface. A wide variety of fish are taken: cormorants are often noticed eating eels, but this may reflect the considerable time taken to subdue an eel and position it for swallowing, rather than any dominance of eels in the diet. In British waters, dive times of 20–30 seconds are common, with a recovery time on the surface around a third of the dive time.
बिबिध रूप
संपादन करीं-
Cranium
-
Drying after fishing
-
Above Farmoor Reservoir, Oxfordshire
-
Colony in Juodkrantė, Lithiuania, and damage to the trees in which they are nesting
-
Drawing by Jos Zwarts
बीडियो
संपादन करीं-
Resting on a post in a port in Den Oever, the Netherlands
-
Stretching wings while sitting on a pole
-
Great cormorant hunting in Odessa
संदर्भ
संपादन करीं- ↑ BirdLife International (2012). "Phalacrocorax carbo". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - ↑ Ali, S. (1993). The Book of Indian Birds. Bombay: Bombay Natural History Society. ISBN 978-0-19-563731-1.
- ↑ Jobling, James A (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. pp. 90, 301. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ↑ उद्धरण खराबी:Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedRibak2005 - ↑ "Cormorant". The Canadian Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 15 December 2017. Retrieved 21 August 2012.
{{cite web}}: External link in|website= - ↑ उद्धरण खराबी:Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedKoffijberg1995 - ↑ Dunning Jr., John B., ed. (1992). CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8493-4258-5.
- ↑ उद्धरण खराबी:Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedHogan1979 - ↑ 9.0 9.1 उद्धरण खराबी:Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedHatch - ↑ उद्धरण खराबी:Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedStevenson
अउरी पढ़ल जाय
संपादन करीं- Sibley, C.G.; Monroe, B.L. (1990). Distribution and taxonomy of birds of the world. New Haven CT: Yale University Press.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Sinclair, Ian; Hockey, Phil; Tarboton, Warwick (2002). SASOL Birds of Southern Africa. Struik. ISBN 1-86872-721-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
- Separation of carbo and sinensis
- Newson, Stuart; Ekins, Graham; Hughes, Baz; Russell, Ian; Sellers, Robin (2005). "Separation of North Atlantic and Continental Cormorants". Birding World. 18 (3): 107–111.
- MIllington, Richard (2005). "Identification of North Atlantic and Continental Cormorants". Birding World. 18 (3): 112–123.
- Murray, T and Cabot, D. (2015). The Breeding Status of Great Cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo carbo) in Co. Wexford. Ir. Nat. J. 34: 89-94.
बाहरी कड़ी
संपादन करीं| विकिमीडिया कॉमंस पर संबंधित मीडिया Phalacrocorax carbo पर मौजूद बा। |
| विकिप्रजाति पर संबंधित जानकारी Phalacrocorax carbo पर मौजूद बाटे। |
- Ageing and sexing (PDF) by Javier Blasco-Zumeta & Gerd-Michael Heinze Archived 2016-03-05 at the Wayback Machine
- Great cormorant Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds
- BirdLife species factsheet for Phalacrocorax carbo
- Phalacrocorax carbo on Avibase
- पनकउआ videos, photos, and sounds at the Internet Bird Collection
- पनकउआ photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- Interactive range map of Phalacrocorax carbo at IUCN Red List maps
- Audio recordings of Great cormorant on Xeno-canto.
